Click here to read what the information on this page means.
| Alternative names | non-conforming Crouzeix–Raviart |
| Abbreviated names | CR |
| Degrees | \(k=1\)
where \(k\) is the polynomial subdegree |
| Polynomial subdegree | \(k\) |
| Polynomial superdegree | triangle: \(k\)
tetrahedron: \(k\)
quadrilateral: \(k+1\)
hexahedron: \(k+1\) |
| Lagrange subdegree | triangle: \(k\)
tetrahedron: \(k\)
quadrilateral: \(k-1\)
hexahedron: \(k-1\) |
| Lagrange superdegree | triangle: \(k\)
tetrahedron: \(k\)
quadrilateral: \(k+1\)
hexahedron: \(k+1\) |
| Reference cells | triangle, tetrahedron, quadrilateral, hexahedron |
| Finite dimensional space | \(\mathcal{P}_{k}\) (triangle, tetrahedron)
\(\mathcal{P}_{k} \oplus \mathcal{Z}^{(13)}_{k}\) (quadrilateral)
\(\mathcal{P}_{k} \oplus \mathcal{Z}^{(14)}_{k}\) (hexahedron)
↓ Show set definitions ↓↑ Hide set definitions ↑\(\mathcal{P}_k=\operatorname{span}\left\{\prod_{i=1}^dx_i^{p_i}\middle|\sum_{i=1}^dp_i\leqslant k\right\}\)
\(\mathcal{Z}^{(13)}_k=\operatorname{span}\left\{(x_1+x_2)(x_1-x_2)\right\}\)
\(\mathcal{Z}^{(14)}_k=\operatorname{span}\left\{(x_1+x_2)(x_1-x_2),(x_2+x_3)(x_2-x_3))\right\}\) |
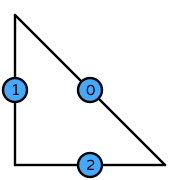
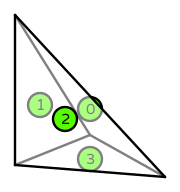
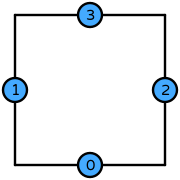
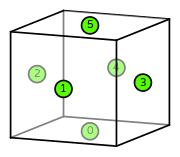
| DOFs | On each facet: point evaluation at midpoint |
| Number of DOFs | triangle: \(3\)
tetrahedron: \(4\)
quadrilateral: \(4\)
hexahedron: \(6\) |
| Mapping | identity |
| continuity | Discontinuous. |
| Categories | Scalar-valued elements |
This element is implemented in
Basix ,
Basix.UFL ,
FIAT , and
Symfem .
↓ Show implementation detail ↓↑ Hide implementation detail ↑| Basix | basix.ElementFamily.CR
↓ Show Basix examples ↓↑ Hide Basix examples ↑Before running this example, you must install Basix: pip install fenics-basix This element can then be created with the following lines of Python: import basix
# Create Crouzeix-Raviart degree 1 on a triangle
element = basix.create_element(basix.ElementFamily.CR, basix.CellType.triangle, 1)
# Create Crouzeix-Raviart degree 1 on a tetrahedron
element = basix.create_element(basix.ElementFamily.CR, basix.CellType.tetrahedron, 1)
# Create Crouzeix-Raviart degree 1 on a quadrilateral
element = basix.create_element(basix.ElementFamily.CR, basix.CellType.quadrilateral, 1)
# Create Crouzeix-Raviart degree 1 on a hexahedron
element = basix.create_element(basix.ElementFamily.CR, basix.CellType.hexahedron, 1) |
| Basix.UFL | basix.ElementFamily.CR
↓ Show Basix.UFL examples ↓↑ Hide Basix.UFL examples ↑Before running this example, you must install Basix.UFL: pip install fenics-ufl
pip install fenics-basix This element can then be created with the following lines of Python: import basix
import basix.ufl
# Create Crouzeix-Raviart degree 1 on a triangle
element = basix.ufl.element(basix.ElementFamily.CR, basix.CellType.triangle, 1)
# Create Crouzeix-Raviart degree 1 on a tetrahedron
element = basix.ufl.element(basix.ElementFamily.CR, basix.CellType.tetrahedron, 1)
# Create Crouzeix-Raviart degree 1 on a quadrilateral
element = basix.ufl.element(basix.ElementFamily.CR, basix.CellType.quadrilateral, 1)
# Create Crouzeix-Raviart degree 1 on a hexahedron
element = basix.ufl.element(basix.ElementFamily.CR, basix.CellType.hexahedron, 1) |
| FIAT | FIAT.CrouzeixRaviart
↓ Show FIAT examples ↓↑ Hide FIAT examples ↑Before running this example, you must install FIAT: pip install firedrake-fiat This element can then be created with the following lines of Python: import FIAT
# Create Crouzeix-Raviart degree 1 on a triangle
element = FIAT.CrouzeixRaviart(FIAT.ufc_cell("triangle"), 1)
# Create Crouzeix-Raviart degree 1 on a tetrahedron
element = FIAT.CrouzeixRaviart(FIAT.ufc_cell("tetrahedron"), 1) Correct: triangle,1; tetrahedron,1 Not implemented: quadrilateral,1; hexahedron,1 |
| Symfem | "Crouzeix-Raviart" (triangle; tetrahedron)
"Rannacher-Turek" (quadrilateral; hexahedron)
↓ Show Symfem examples ↓↑ Hide Symfem examples ↑Before running this example, you must install Symfem: pip install symfem This element can then be created with the following lines of Python: import symfem
# Create Crouzeix-Raviart degree 1 on a triangle
element = symfem.create_element("triangle", "Crouzeix-Raviart", 1)
# Create Crouzeix-Raviart degree 1 on a tetrahedron
element = symfem.create_element("tetrahedron", "Crouzeix-Raviart", 1)
# Create Crouzeix-Raviart degree 1 on a quadrilateral
element = symfem.create_element("quadrilateral", "Rannacher-Turek", 1)
# Create Crouzeix-Raviart degree 1 on a hexahedron
element = symfem.create_element("hexahedron", "Rannacher-Turek", 1) |
- [1] Crouzeix, Michel and Raviart, Pierre-Arnaud. Conforming and nonconforming finite element methods for solving the stationary Stokes equations, Revue Française d'Automatique, Informatique et Recherche Opérationnelle 3, 33–75, 1973. [DOI: 10.1051/m2an/197307R300331] [BibTeX]
- [2] Rannacher, Rolf and Turek, Stefan. Simple nonconforming quadrilateral Stokes element, Numerical methods for partial differential equations 8, 97–111, 1992. [DOI: 10.1002/num.1690080202] [BibTeX]
| Element added | 01 January 2021 |
| Element last updated | 17 November 2025 |