an encyclopedia of finite element definitions
Degree 3 Arnold–Winther on a triangle
◀ Back to Arnold–Winther definition page
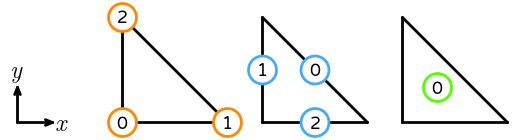
- \(R\) is the reference triangle. The following numbering of the sub-entities of the reference cell is used:
- \(\mathcal{V}\) is spanned by: \(\left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 1&\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right)\), \(\left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle 1\\\displaystyle 1&\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right)\), \(\left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle 1\end{array}\right)\), \(\left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle x&\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right)\), \(\left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle x\\\displaystyle x&\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right)\), \(\left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle x\end{array}\right)\), \(\left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle x^{2}&\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right)\), \(\left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle x^{2}\\\displaystyle x^{2}&\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right)\), \(\left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle x^{2}\end{array}\right)\), \(\left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle x^{3}&\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right)\), \(\left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle x^{3}\\\displaystyle x^{3}&\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right)\), \(\left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle x^{3}\end{array}\right)\), \(\left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle y&\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right)\), \(\left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle y\\\displaystyle y&\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right)\), \(\left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle y\end{array}\right)\), \(\left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle x y&\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right)\), \(\left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle x y\\\displaystyle x y&\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right)\), \(\left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle x y\end{array}\right)\), \(\left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle x^{2} y&\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right)\), \(\left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle x^{2} y\\\displaystyle x^{2} y&\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right)\), \(\left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle x^{2} y\end{array}\right)\), \(\left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle y^{2}&\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right)\), \(\left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle y^{2}\\\displaystyle y^{2}&\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right)\), \(\left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle y^{2}\end{array}\right)\), \(\left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle x y^{2}&\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right)\), \(\left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle x y^{2}\\\displaystyle x y^{2}&\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right)\), \(\left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle x y^{2}\end{array}\right)\), \(\left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle y^{3}&\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right)\), \(\left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle y^{3}\\\displaystyle y^{3}&\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right)\), \(\left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle y^{3}\end{array}\right)\), \(\left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 30 y^{4}&\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right)\), \(\left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 20 x y^{3}&\displaystyle - 5 y^{4}\\\displaystyle - 5 y^{4}&\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right)\), \(\left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 12 x^{2} y^{2}&\displaystyle - 8 x y^{3}\\\displaystyle - 8 x y^{3}&\displaystyle 2 y^{4}\end{array}\right)\), \(\left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 6 x^{3} y&\displaystyle - 9 x^{2} y^{2}\\\displaystyle - 9 x^{2} y^{2}&\displaystyle 6 x y^{3}\end{array}\right)\), \(\left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 2 x^{4}&\displaystyle - 8 x^{3} y\\\displaystyle - 8 x^{3} y&\displaystyle 12 x^{2} y^{2}\end{array}\right)\), \(\left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle x^{4}\\\displaystyle x^{4}&\displaystyle - 4 x^{3} y\end{array}\right)\), \(\left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle x^{4}\end{array}\right)\)
- \(\mathcal{L}=\{l_0,...,l_{36}\}\)
- Functionals and basis functions:
\(\displaystyle l_{0}:\mathbf{V}\mapsto\left(\begin{array}{c}1\\0\end{array}\right)^{\text{t}}\mathbf{V}(0,0)\left(\begin{array}{c}1\\0\end{array}\right)\)
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{0} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle - \frac{x^{4}}{3} - 16 x^{3} y + \frac{8 x^{3}}{3} - 44 x^{2} y^{2} + 32 x^{2} y - \frac{10 x^{2}}{3} + 35 y^{4} - 80 y^{3} + 60 y^{2} - 16 y + 1&\displaystyle \frac{4 x y \left(x^{2} + 18 x y - 6 x + 22 y^{2} - 24 y + 5\right)}{3}\\\displaystyle \frac{4 x y \left(x^{2} + 18 x y - 6 x + 22 y^{2} - 24 y + 5\right)}{3}&\displaystyle \frac{2 y^{2} \left(- 3 x^{2} - 24 x y + 12 x - 11 y^{2} + 16 y - 5\right)}{3}\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with vertex 0 of the reference cell.
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{0} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle - \frac{x^{4}}{3} - 16 x^{3} y + \frac{8 x^{3}}{3} - 44 x^{2} y^{2} + 32 x^{2} y - \frac{10 x^{2}}{3} + 35 y^{4} - 80 y^{3} + 60 y^{2} - 16 y + 1&\displaystyle \frac{4 x y \left(x^{2} + 18 x y - 6 x + 22 y^{2} - 24 y + 5\right)}{3}\\\displaystyle \frac{4 x y \left(x^{2} + 18 x y - 6 x + 22 y^{2} - 24 y + 5\right)}{3}&\displaystyle \frac{2 y^{2} \left(- 3 x^{2} - 24 x y + 12 x - 11 y^{2} + 16 y - 5\right)}{3}\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with vertex 0 of the reference cell.
\(\displaystyle l_{1}:\mathbf{V}\mapsto\left(\begin{array}{c}1\\0\end{array}\right)^{\text{t}}\mathbf{V}(0,0)\left(\begin{array}{c}0\\1\end{array}\right)\)
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{1} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 2 x \left(- 23 x^{3} - 96 x^{2} y + 50 x^{2} - 138 x y^{2} + 150 x y - 35 x - 70 y^{3} + 120 y^{2} - 60 y + 8\right)&\displaystyle 35 x^{4} + 184 x^{3} y - 80 x^{3} + 288 x^{2} y^{2} - 300 x^{2} y + 60 x^{2} + 184 x y^{3} - 300 x y^{2} + 140 x y - 16 x + 35 y^{4} - 80 y^{3} + 60 y^{2} - 16 y + 1\\\displaystyle 35 x^{4} + 184 x^{3} y - 80 x^{3} + 288 x^{2} y^{2} - 300 x^{2} y + 60 x^{2} + 184 x y^{3} - 300 x y^{2} + 140 x y - 16 x + 35 y^{4} - 80 y^{3} + 60 y^{2} - 16 y + 1&\displaystyle 2 y \left(- 70 x^{3} - 138 x^{2} y + 120 x^{2} - 96 x y^{2} + 150 x y - 60 x - 23 y^{3} + 50 y^{2} - 35 y + 8\right)\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with vertex 0 of the reference cell.
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{1} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 2 x \left(- 23 x^{3} - 96 x^{2} y + 50 x^{2} - 138 x y^{2} + 150 x y - 35 x - 70 y^{3} + 120 y^{2} - 60 y + 8\right)&\displaystyle 35 x^{4} + 184 x^{3} y - 80 x^{3} + 288 x^{2} y^{2} - 300 x^{2} y + 60 x^{2} + 184 x y^{3} - 300 x y^{2} + 140 x y - 16 x + 35 y^{4} - 80 y^{3} + 60 y^{2} - 16 y + 1\\\displaystyle 35 x^{4} + 184 x^{3} y - 80 x^{3} + 288 x^{2} y^{2} - 300 x^{2} y + 60 x^{2} + 184 x y^{3} - 300 x y^{2} + 140 x y - 16 x + 35 y^{4} - 80 y^{3} + 60 y^{2} - 16 y + 1&\displaystyle 2 y \left(- 70 x^{3} - 138 x^{2} y + 120 x^{2} - 96 x y^{2} + 150 x y - 60 x - 23 y^{3} + 50 y^{2} - 35 y + 8\right)\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with vertex 0 of the reference cell.
\(\displaystyle l_{2}:\mathbf{V}\mapsto\left(\begin{array}{c}0\\1\end{array}\right)^{\text{t}}\mathbf{V}(0,0)\left(\begin{array}{c}0\\1\end{array}\right)\)
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{2} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle \frac{2 x^{2} \left(- 11 x^{2} - 24 x y + 16 x - 3 y^{2} + 12 y - 5\right)}{3}&\displaystyle \frac{4 x y \left(22 x^{2} + 18 x y - 24 x + y^{2} - 6 y + 5\right)}{3}\\\displaystyle \frac{4 x y \left(22 x^{2} + 18 x y - 24 x + y^{2} - 6 y + 5\right)}{3}&\displaystyle 35 x^{4} - 80 x^{3} - 44 x^{2} y^{2} + 60 x^{2} - 16 x y^{3} + 32 x y^{2} - 16 x - \frac{y^{4}}{3} + \frac{8 y^{3}}{3} - \frac{10 y^{2}}{3} + 1\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with vertex 0 of the reference cell.
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{2} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle \frac{2 x^{2} \left(- 11 x^{2} - 24 x y + 16 x - 3 y^{2} + 12 y - 5\right)}{3}&\displaystyle \frac{4 x y \left(22 x^{2} + 18 x y - 24 x + y^{2} - 6 y + 5\right)}{3}\\\displaystyle \frac{4 x y \left(22 x^{2} + 18 x y - 24 x + y^{2} - 6 y + 5\right)}{3}&\displaystyle 35 x^{4} - 80 x^{3} - 44 x^{2} y^{2} + 60 x^{2} - 16 x y^{3} + 32 x y^{2} - 16 x - \frac{y^{4}}{3} + \frac{8 y^{3}}{3} - \frac{10 y^{2}}{3} + 1\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with vertex 0 of the reference cell.
\(\displaystyle l_{3}:\mathbf{V}\mapsto\left(\begin{array}{c}1\\0\end{array}\right)^{\text{t}}\mathbf{V}(1,0)\left(\begin{array}{c}1\\0\end{array}\right)\)
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{3} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle x^{2} \left(- 3 x^{2} - 4 x y + 4 x + 24 y^{2} - 12 y\right)&\displaystyle 2 x y \left(6 x^{2} + 3 x y - 6 x - 8 y^{2} + 6 y\right)\\\displaystyle 2 x y \left(6 x^{2} + 3 x y - 6 x - 8 y^{2} + 6 y\right)&\displaystyle y^{2} \left(- 18 x^{2} - 4 x y + 12 x + 4 y^{2} - 4 y\right)\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with vertex 1 of the reference cell.
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{3} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle x^{2} \left(- 3 x^{2} - 4 x y + 4 x + 24 y^{2} - 12 y\right)&\displaystyle 2 x y \left(6 x^{2} + 3 x y - 6 x - 8 y^{2} + 6 y\right)\\\displaystyle 2 x y \left(6 x^{2} + 3 x y - 6 x - 8 y^{2} + 6 y\right)&\displaystyle y^{2} \left(- 18 x^{2} - 4 x y + 12 x + 4 y^{2} - 4 y\right)\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with vertex 1 of the reference cell.
\(\displaystyle l_{4}:\mathbf{V}\mapsto\left(\begin{array}{c}1\\0\end{array}\right)^{\text{t}}\mathbf{V}(1,0)\left(\begin{array}{c}0\\1\end{array}\right)\)
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{4} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle \frac{x^{2} \left(- 47 x^{2} - 58 x y + 62 x + 54 y^{2} - 6 y - 15\right)}{2}&\displaystyle \frac{x \left(70 x^{3} + 188 x^{2} y - 120 x^{2} + 87 x y^{2} - 186 x y + 60 x - 36 y^{3} + 6 y^{2} + 30 y - 8\right)}{2}\\\displaystyle \frac{x \left(70 x^{3} + 188 x^{2} y - 120 x^{2} + 87 x y^{2} - 186 x y + 60 x - 36 y^{3} + 6 y^{2} + 30 y - 8\right)}{2}&\displaystyle \frac{y \left(- 280 x^{3} - 282 x^{2} y + 360 x^{2} - 58 x y^{2} + 186 x y - 120 x + 9 y^{3} - 2 y^{2} - 15 y + 8\right)}{2}\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with vertex 1 of the reference cell.
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{4} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle \frac{x^{2} \left(- 47 x^{2} - 58 x y + 62 x + 54 y^{2} - 6 y - 15\right)}{2}&\displaystyle \frac{x \left(70 x^{3} + 188 x^{2} y - 120 x^{2} + 87 x y^{2} - 186 x y + 60 x - 36 y^{3} + 6 y^{2} + 30 y - 8\right)}{2}\\\displaystyle \frac{x \left(70 x^{3} + 188 x^{2} y - 120 x^{2} + 87 x y^{2} - 186 x y + 60 x - 36 y^{3} + 6 y^{2} + 30 y - 8\right)}{2}&\displaystyle \frac{y \left(- 280 x^{3} - 282 x^{2} y + 360 x^{2} - 58 x y^{2} + 186 x y - 120 x + 9 y^{3} - 2 y^{2} - 15 y + 8\right)}{2}\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with vertex 1 of the reference cell.
\(\displaystyle l_{5}:\mathbf{V}\mapsto\left(\begin{array}{c}0\\1\end{array}\right)^{\text{t}}\mathbf{V}(1,0)\left(\begin{array}{c}0\\1\end{array}\right)\)
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{5} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle \frac{5 x^{2} \left(x^{2} + 6 x y - 2 x + 6 y^{2} - 6 y + 1\right)}{6}&\displaystyle \frac{5 x y \left(- 4 x^{2} - 9 x y + 6 x - 4 y^{2} + 6 y - 2\right)}{6}\\\displaystyle \frac{5 x y \left(- 4 x^{2} - 9 x y + 6 x - 4 y^{2} + 6 y - 2\right)}{6}&\displaystyle 35 x^{4} - 60 x^{3} + 5 x^{2} y^{2} + 30 x^{2} + 5 x y^{3} - 5 x y^{2} - 4 x + \frac{5 y^{4}}{6} - \frac{5 y^{3}}{3} + \frac{5 y^{2}}{6}\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with vertex 1 of the reference cell.
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{5} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle \frac{5 x^{2} \left(x^{2} + 6 x y - 2 x + 6 y^{2} - 6 y + 1\right)}{6}&\displaystyle \frac{5 x y \left(- 4 x^{2} - 9 x y + 6 x - 4 y^{2} + 6 y - 2\right)}{6}\\\displaystyle \frac{5 x y \left(- 4 x^{2} - 9 x y + 6 x - 4 y^{2} + 6 y - 2\right)}{6}&\displaystyle 35 x^{4} - 60 x^{3} + 5 x^{2} y^{2} + 30 x^{2} + 5 x y^{3} - 5 x y^{2} - 4 x + \frac{5 y^{4}}{6} - \frac{5 y^{3}}{3} + \frac{5 y^{2}}{6}\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with vertex 1 of the reference cell.
\(\displaystyle l_{6}:\mathbf{V}\mapsto\left(\begin{array}{c}1\\0\end{array}\right)^{\text{t}}\mathbf{V}(0,1)\left(\begin{array}{c}1\\0\end{array}\right)\)
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{6} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle \frac{5 x^{4}}{6} + 5 x^{3} y - \frac{5 x^{3}}{3} + 5 x^{2} y^{2} - 5 x^{2} y + \frac{5 x^{2}}{6} + 35 y^{4} - 60 y^{3} + 30 y^{2} - 4 y&\displaystyle \frac{5 x y \left(- 4 x^{2} - 9 x y + 6 x - 4 y^{2} + 6 y - 2\right)}{6}\\\displaystyle \frac{5 x y \left(- 4 x^{2} - 9 x y + 6 x - 4 y^{2} + 6 y - 2\right)}{6}&\displaystyle \frac{5 y^{2} \left(6 x^{2} + 6 x y - 6 x + y^{2} - 2 y + 1\right)}{6}\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with vertex 2 of the reference cell.
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{6} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle \frac{5 x^{4}}{6} + 5 x^{3} y - \frac{5 x^{3}}{3} + 5 x^{2} y^{2} - 5 x^{2} y + \frac{5 x^{2}}{6} + 35 y^{4} - 60 y^{3} + 30 y^{2} - 4 y&\displaystyle \frac{5 x y \left(- 4 x^{2} - 9 x y + 6 x - 4 y^{2} + 6 y - 2\right)}{6}\\\displaystyle \frac{5 x y \left(- 4 x^{2} - 9 x y + 6 x - 4 y^{2} + 6 y - 2\right)}{6}&\displaystyle \frac{5 y^{2} \left(6 x^{2} + 6 x y - 6 x + y^{2} - 2 y + 1\right)}{6}\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with vertex 2 of the reference cell.
\(\displaystyle l_{7}:\mathbf{V}\mapsto\left(\begin{array}{c}1\\0\end{array}\right)^{\text{t}}\mathbf{V}(0,1)\left(\begin{array}{c}0\\1\end{array}\right)\)
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{7} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle \frac{x \left(9 x^{3} - 58 x^{2} y - 2 x^{2} - 282 x y^{2} + 186 x y - 15 x - 280 y^{3} + 360 y^{2} - 120 y + 8\right)}{2}&\displaystyle \frac{y \left(- 36 x^{3} + 87 x^{2} y + 6 x^{2} + 188 x y^{2} - 186 x y + 30 x + 70 y^{3} - 120 y^{2} + 60 y - 8\right)}{2}\\\displaystyle \frac{y \left(- 36 x^{3} + 87 x^{2} y + 6 x^{2} + 188 x y^{2} - 186 x y + 30 x + 70 y^{3} - 120 y^{2} + 60 y - 8\right)}{2}&\displaystyle \frac{y^{2} \left(54 x^{2} - 58 x y - 6 x - 47 y^{2} + 62 y - 15\right)}{2}\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with vertex 2 of the reference cell.
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{7} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle \frac{x \left(9 x^{3} - 58 x^{2} y - 2 x^{2} - 282 x y^{2} + 186 x y - 15 x - 280 y^{3} + 360 y^{2} - 120 y + 8\right)}{2}&\displaystyle \frac{y \left(- 36 x^{3} + 87 x^{2} y + 6 x^{2} + 188 x y^{2} - 186 x y + 30 x + 70 y^{3} - 120 y^{2} + 60 y - 8\right)}{2}\\\displaystyle \frac{y \left(- 36 x^{3} + 87 x^{2} y + 6 x^{2} + 188 x y^{2} - 186 x y + 30 x + 70 y^{3} - 120 y^{2} + 60 y - 8\right)}{2}&\displaystyle \frac{y^{2} \left(54 x^{2} - 58 x y - 6 x - 47 y^{2} + 62 y - 15\right)}{2}\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with vertex 2 of the reference cell.
\(\displaystyle l_{8}:\mathbf{V}\mapsto\left(\begin{array}{c}0\\1\end{array}\right)^{\text{t}}\mathbf{V}(0,1)\left(\begin{array}{c}0\\1\end{array}\right)\)
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{8} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle x^{2} \left(4 x^{2} - 4 x y - 4 x - 18 y^{2} + 12 y\right)&\displaystyle 2 x y \left(- 8 x^{2} + 3 x y + 6 x + 6 y^{2} - 6 y\right)\\\displaystyle 2 x y \left(- 8 x^{2} + 3 x y + 6 x + 6 y^{2} - 6 y\right)&\displaystyle y^{2} \left(24 x^{2} - 4 x y - 12 x - 3 y^{2} + 4 y\right)\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with vertex 2 of the reference cell.
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{8} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle x^{2} \left(4 x^{2} - 4 x y - 4 x - 18 y^{2} + 12 y\right)&\displaystyle 2 x y \left(- 8 x^{2} + 3 x y + 6 x + 6 y^{2} - 6 y\right)\\\displaystyle 2 x y \left(- 8 x^{2} + 3 x y + 6 x + 6 y^{2} - 6 y\right)&\displaystyle y^{2} \left(24 x^{2} - 4 x y - 12 x - 3 y^{2} + 4 y\right)\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with vertex 2 of the reference cell.
\(\displaystyle l_{9}:\boldsymbol{V}\mapsto\displaystyle\int_{e_{0}}(2 s_{0}^{2} - 3 s_{0} + 1)\left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle 1\end{array}\right)^{\text{t}}\boldsymbol{V}\left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle 1\end{array}\right)\)
where \(e_{0}\) is the 0th edge;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(e_{0}\).
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{9} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle x^{2} \left(88 x^{2} + 192 x y - 128 x + 24 y^{2} - 96 y + 40\right)&\displaystyle 16 x y \left(- 22 x^{2} - 18 x y + 24 x - y^{2} + 6 y - 5\right)\\\displaystyle 16 x y \left(- 22 x^{2} - 18 x y + 24 x - y^{2} + 6 y - 5\right)&\displaystyle - 420 x^{4} + 900 x^{3} + 528 x^{2} y^{2} - 180 x^{2} y - 600 x^{2} + 192 x y^{3} - 564 x y^{2} + 240 x y + 120 x + 4 y^{4} - 92 y^{3} + 160 y^{2} - 72 y\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with edge 0 of the reference cell.
where \(e_{0}\) is the 0th edge;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(e_{0}\).
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{9} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle x^{2} \left(88 x^{2} + 192 x y - 128 x + 24 y^{2} - 96 y + 40\right)&\displaystyle 16 x y \left(- 22 x^{2} - 18 x y + 24 x - y^{2} + 6 y - 5\right)\\\displaystyle 16 x y \left(- 22 x^{2} - 18 x y + 24 x - y^{2} + 6 y - 5\right)&\displaystyle - 420 x^{4} + 900 x^{3} + 528 x^{2} y^{2} - 180 x^{2} y - 600 x^{2} + 192 x y^{3} - 564 x y^{2} + 240 x y + 120 x + 4 y^{4} - 92 y^{3} + 160 y^{2} - 72 y\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with edge 0 of the reference cell.
\(\displaystyle l_{10}:\boldsymbol{V}\mapsto\displaystyle\int_{e_{0}}(2 s_{0}^{2} - 3 s_{0} + 1)\left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle 1\\\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right)^{\text{t}}\boldsymbol{V}\left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle 1\end{array}\right)\)
where \(e_{0}\) is the 0th edge;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(e_{0}\).
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{10} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 12 x \left(37 x^{3} + 96 x^{2} y - 71 x^{2} + 54 x y^{2} - 102 x y + 40 x - 15 y^{2} + 20 y - 6\right)&\displaystyle 12 x \left(- 35 x^{3} - 148 x^{2} y + 75 x^{2} - 144 x y^{2} + 198 x y - 50 x - 36 y^{3} + 87 y^{2} - 60 y + 10\right)\\\displaystyle 12 x \left(- 35 x^{3} - 148 x^{2} y + 75 x^{2} - 144 x y^{2} + 198 x y - 50 x - 36 y^{3} + 87 y^{2} - 60 y + 10\right)&\displaystyle 12 y \left(140 x^{3} + 222 x^{2} y - 225 x^{2} + 96 x y^{2} - 198 x y + 100 x + 9 y^{3} - 29 y^{2} + 30 y - 10\right)\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with edge 0 of the reference cell.
where \(e_{0}\) is the 0th edge;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(e_{0}\).
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{10} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 12 x \left(37 x^{3} + 96 x^{2} y - 71 x^{2} + 54 x y^{2} - 102 x y + 40 x - 15 y^{2} + 20 y - 6\right)&\displaystyle 12 x \left(- 35 x^{3} - 148 x^{2} y + 75 x^{2} - 144 x y^{2} + 198 x y - 50 x - 36 y^{3} + 87 y^{2} - 60 y + 10\right)\\\displaystyle 12 x \left(- 35 x^{3} - 148 x^{2} y + 75 x^{2} - 144 x y^{2} + 198 x y - 50 x - 36 y^{3} + 87 y^{2} - 60 y + 10\right)&\displaystyle 12 y \left(140 x^{3} + 222 x^{2} y - 225 x^{2} + 96 x y^{2} - 198 x y + 100 x + 9 y^{3} - 29 y^{2} + 30 y - 10\right)\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with edge 0 of the reference cell.
\(\displaystyle l_{11}:\boldsymbol{V}\mapsto\displaystyle\int_{e_{0}}(s_{0} \left(2 s_{0} - 1\right))\left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle 1\end{array}\right)^{\text{t}}\boldsymbol{V}\left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle 1\end{array}\right)\)
where \(e_{0}\) is the 0th edge;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(e_{0}\).
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{11} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle x^{2} \left(63 x^{2} + 42 x y - 78 x - 126 y^{2} + 54 y + 15\right)&\displaystyle 3 x y \left(- 84 x^{2} - 21 x y + 78 x + 28 y^{2} - 18 y - 10\right)\\\displaystyle 3 x y \left(- 84 x^{2} - 21 x y + 78 x + 28 y^{2} - 18 y - 10\right)&\displaystyle - 420 x^{4} + 780 x^{3} + 378 x^{2} y^{2} - 180 x^{2} y - 420 x^{2} + 42 x y^{3} - 234 x y^{2} + 120 x y + 60 x - 21 y^{4} + 18 y^{3} + 15 y^{2} - 12 y\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with edge 0 of the reference cell.
where \(e_{0}\) is the 0th edge;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(e_{0}\).
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{11} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle x^{2} \left(63 x^{2} + 42 x y - 78 x - 126 y^{2} + 54 y + 15\right)&\displaystyle 3 x y \left(- 84 x^{2} - 21 x y + 78 x + 28 y^{2} - 18 y - 10\right)\\\displaystyle 3 x y \left(- 84 x^{2} - 21 x y + 78 x + 28 y^{2} - 18 y - 10\right)&\displaystyle - 420 x^{4} + 780 x^{3} + 378 x^{2} y^{2} - 180 x^{2} y - 420 x^{2} + 42 x y^{3} - 234 x y^{2} + 120 x y + 60 x - 21 y^{4} + 18 y^{3} + 15 y^{2} - 12 y\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with edge 0 of the reference cell.
\(\displaystyle l_{12}:\boldsymbol{V}\mapsto\displaystyle\int_{e_{0}}(s_{0} \left(2 s_{0} - 1\right))\left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle 1\\\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right)^{\text{t}}\boldsymbol{V}\left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle 1\end{array}\right)\)
where \(e_{0}\) is the 0th edge;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(e_{0}\).
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{12} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle x \left(319 x^{3} + 402 x^{2} y - 482 x^{2} - 102 x y^{2} - 114 x y + 175 x - 12\right)&\displaystyle x \left(- 420 x^{3} - 1276 x^{2} y + 780 x^{2} - 603 x y^{2} + 1266 x y - 420 x + 68 y^{3} + 114 y^{2} - 230 y + 60\right)\\\displaystyle x \left(- 420 x^{3} - 1276 x^{2} y + 780 x^{2} - 603 x y^{2} + 1266 x y - 420 x + 68 y^{3} + 114 y^{2} - 230 y + 60\right)&\displaystyle y \left(1680 x^{3} + 1914 x^{2} y - 2340 x^{2} + 402 x y^{2} - 1266 x y + 840 x - 17 y^{3} - 38 y^{2} + 115 y - 60\right)\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with edge 0 of the reference cell.
where \(e_{0}\) is the 0th edge;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(e_{0}\).
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{12} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle x \left(319 x^{3} + 402 x^{2} y - 482 x^{2} - 102 x y^{2} - 114 x y + 175 x - 12\right)&\displaystyle x \left(- 420 x^{3} - 1276 x^{2} y + 780 x^{2} - 603 x y^{2} + 1266 x y - 420 x + 68 y^{3} + 114 y^{2} - 230 y + 60\right)\\\displaystyle x \left(- 420 x^{3} - 1276 x^{2} y + 780 x^{2} - 603 x y^{2} + 1266 x y - 420 x + 68 y^{3} + 114 y^{2} - 230 y + 60\right)&\displaystyle y \left(1680 x^{3} + 1914 x^{2} y - 2340 x^{2} + 402 x y^{2} - 1266 x y + 840 x - 17 y^{3} - 38 y^{2} + 115 y - 60\right)\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with edge 0 of the reference cell.
\(\displaystyle l_{13}:\boldsymbol{V}\mapsto\displaystyle\int_{e_{0}}(4 s_{0} \left(1 - s_{0}\right))\left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle 1\end{array}\right)^{\text{t}}\boldsymbol{V}\left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle 1\end{array}\right)\)
where \(e_{0}\) is the 0th edge;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(e_{0}\).
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{13} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle x^{2} \left(- 22 x^{2} - 48 x y + 32 x - 6 y^{2} + 24 y - 10\right)&\displaystyle 4 x y \left(22 x^{2} + 18 x y - 24 x + y^{2} - 6 y + 5\right)\\\displaystyle 4 x y \left(22 x^{2} + 18 x y - 24 x + y^{2} - 6 y + 5\right)&\displaystyle 105 x^{4} - 210 x^{3} - 132 x^{2} y^{2} + 90 x^{2} y + 120 x^{2} - 48 x y^{3} + 141 x y^{2} - 90 x y - 15 x - y^{4} - 7 y^{3} + 5 y^{2} + 3 y\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with edge 0 of the reference cell.
where \(e_{0}\) is the 0th edge;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(e_{0}\).
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{13} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle x^{2} \left(- 22 x^{2} - 48 x y + 32 x - 6 y^{2} + 24 y - 10\right)&\displaystyle 4 x y \left(22 x^{2} + 18 x y - 24 x + y^{2} - 6 y + 5\right)\\\displaystyle 4 x y \left(22 x^{2} + 18 x y - 24 x + y^{2} - 6 y + 5\right)&\displaystyle 105 x^{4} - 210 x^{3} - 132 x^{2} y^{2} + 90 x^{2} y + 120 x^{2} - 48 x y^{3} + 141 x y^{2} - 90 x y - 15 x - y^{4} - 7 y^{3} + 5 y^{2} + 3 y\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with edge 0 of the reference cell.
\(\displaystyle l_{14}:\boldsymbol{V}\mapsto\displaystyle\int_{e_{0}}(4 s_{0} \left(1 - s_{0}\right))\left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle 1\\\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right)^{\text{t}}\boldsymbol{V}\left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle 1\end{array}\right)\)
where \(e_{0}\) is the 0th edge;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(e_{0}\).
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{14} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle \frac{x \left(- 319 x^{3} - 402 x^{2} y + 542 x^{2} + 102 x y^{2} + 114 x y - 235 x - 180 y^{2} + 120 y + 12\right)}{4}&\displaystyle \frac{x \left(420 x^{3} + 1276 x^{2} y - 840 x^{2} + 603 x y^{2} - 1266 x y + 480 x - 68 y^{3} + 66 y^{2} + 110 y - 60\right)}{4}\\\displaystyle \frac{x \left(420 x^{3} + 1276 x^{2} y - 840 x^{2} + 603 x y^{2} - 1266 x y + 480 x - 68 y^{3} + 66 y^{2} + 110 y - 60\right)}{4}&\displaystyle \frac{y \left(- 1680 x^{3} - 1914 x^{2} y + 2520 x^{2} - 402 x y^{2} + 1266 x y - 960 x + 17 y^{3} - 22 y^{2} - 55 y + 60\right)}{4}\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with edge 0 of the reference cell.
where \(e_{0}\) is the 0th edge;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(e_{0}\).
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{14} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle \frac{x \left(- 319 x^{3} - 402 x^{2} y + 542 x^{2} + 102 x y^{2} + 114 x y - 235 x - 180 y^{2} + 120 y + 12\right)}{4}&\displaystyle \frac{x \left(420 x^{3} + 1276 x^{2} y - 840 x^{2} + 603 x y^{2} - 1266 x y + 480 x - 68 y^{3} + 66 y^{2} + 110 y - 60\right)}{4}\\\displaystyle \frac{x \left(420 x^{3} + 1276 x^{2} y - 840 x^{2} + 603 x y^{2} - 1266 x y + 480 x - 68 y^{3} + 66 y^{2} + 110 y - 60\right)}{4}&\displaystyle \frac{y \left(- 1680 x^{3} - 1914 x^{2} y + 2520 x^{2} - 402 x y^{2} + 1266 x y - 960 x + 17 y^{3} - 22 y^{2} - 55 y + 60\right)}{4}\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with edge 0 of the reference cell.
\(\displaystyle l_{15}:\boldsymbol{V}\mapsto\displaystyle\int_{e_{1}}(2 s_{0}^{2} - 3 s_{0} + 1)\left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle -1\\\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right)^{\text{t}}\boldsymbol{V}\left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle -1\\\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right)\)
where \(e_{1}\) is the 1st edge;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(e_{1}\).
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{15} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 4 x^{4} + 192 x^{3} y - 92 x^{3} + 528 x^{2} y^{2} - 564 x^{2} y + 160 x^{2} - 180 x y^{2} + 240 x y - 72 x - 420 y^{4} + 900 y^{3} - 600 y^{2} + 120 y&\displaystyle 16 x y \left(- x^{2} - 18 x y + 6 x - 22 y^{2} + 24 y - 5\right)\\\displaystyle 16 x y \left(- x^{2} - 18 x y + 6 x - 22 y^{2} + 24 y - 5\right)&\displaystyle y^{2} \left(24 x^{2} + 192 x y - 96 x + 88 y^{2} - 128 y + 40\right)\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with edge 1 of the reference cell.
where \(e_{1}\) is the 1st edge;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(e_{1}\).
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{15} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 4 x^{4} + 192 x^{3} y - 92 x^{3} + 528 x^{2} y^{2} - 564 x^{2} y + 160 x^{2} - 180 x y^{2} + 240 x y - 72 x - 420 y^{4} + 900 y^{3} - 600 y^{2} + 120 y&\displaystyle 16 x y \left(- x^{2} - 18 x y + 6 x - 22 y^{2} + 24 y - 5\right)\\\displaystyle 16 x y \left(- x^{2} - 18 x y + 6 x - 22 y^{2} + 24 y - 5\right)&\displaystyle y^{2} \left(24 x^{2} + 192 x y - 96 x + 88 y^{2} - 128 y + 40\right)\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with edge 1 of the reference cell.
\(\displaystyle l_{16}:\boldsymbol{V}\mapsto\displaystyle\int_{e_{1}}(2 s_{0}^{2} - 3 s_{0} + 1)\left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle 1\end{array}\right)^{\text{t}}\boldsymbol{V}\left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle -1\\\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right)\)
where \(e_{1}\) is the 1st edge;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(e_{1}\).
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{16} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 12 x \left(- 9 x^{3} - 96 x^{2} y + 29 x^{2} - 222 x y^{2} + 198 x y - 30 x - 140 y^{3} + 225 y^{2} - 100 y + 10\right)&\displaystyle 12 y \left(36 x^{3} + 144 x^{2} y - 87 x^{2} + 148 x y^{2} - 198 x y + 60 x + 35 y^{3} - 75 y^{2} + 50 y - 10\right)\\\displaystyle 12 y \left(36 x^{3} + 144 x^{2} y - 87 x^{2} + 148 x y^{2} - 198 x y + 60 x + 35 y^{3} - 75 y^{2} + 50 y - 10\right)&\displaystyle 12 y \left(- 54 x^{2} y + 15 x^{2} - 96 x y^{2} + 102 x y - 20 x - 37 y^{3} + 71 y^{2} - 40 y + 6\right)\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with edge 1 of the reference cell.
where \(e_{1}\) is the 1st edge;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(e_{1}\).
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{16} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 12 x \left(- 9 x^{3} - 96 x^{2} y + 29 x^{2} - 222 x y^{2} + 198 x y - 30 x - 140 y^{3} + 225 y^{2} - 100 y + 10\right)&\displaystyle 12 y \left(36 x^{3} + 144 x^{2} y - 87 x^{2} + 148 x y^{2} - 198 x y + 60 x + 35 y^{3} - 75 y^{2} + 50 y - 10\right)\\\displaystyle 12 y \left(36 x^{3} + 144 x^{2} y - 87 x^{2} + 148 x y^{2} - 198 x y + 60 x + 35 y^{3} - 75 y^{2} + 50 y - 10\right)&\displaystyle 12 y \left(- 54 x^{2} y + 15 x^{2} - 96 x y^{2} + 102 x y - 20 x - 37 y^{3} + 71 y^{2} - 40 y + 6\right)\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with edge 1 of the reference cell.
\(\displaystyle l_{17}:\boldsymbol{V}\mapsto\displaystyle\int_{e_{1}}(s_{0} \left(2 s_{0} - 1\right))\left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle -1\\\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right)^{\text{t}}\boldsymbol{V}\left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle -1\\\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right)\)
where \(e_{1}\) is the 1st edge;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(e_{1}\).
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{17} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle - 21 x^{4} + 42 x^{3} y + 18 x^{3} + 378 x^{2} y^{2} - 234 x^{2} y + 15 x^{2} - 180 x y^{2} + 120 x y - 12 x - 420 y^{4} + 780 y^{3} - 420 y^{2} + 60 y&\displaystyle 3 x y \left(28 x^{2} - 21 x y - 18 x - 84 y^{2} + 78 y - 10\right)\\\displaystyle 3 x y \left(28 x^{2} - 21 x y - 18 x - 84 y^{2} + 78 y - 10\right)&\displaystyle y^{2} \left(- 126 x^{2} + 42 x y + 54 x + 63 y^{2} - 78 y + 15\right)\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with edge 1 of the reference cell.
where \(e_{1}\) is the 1st edge;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(e_{1}\).
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{17} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle - 21 x^{4} + 42 x^{3} y + 18 x^{3} + 378 x^{2} y^{2} - 234 x^{2} y + 15 x^{2} - 180 x y^{2} + 120 x y - 12 x - 420 y^{4} + 780 y^{3} - 420 y^{2} + 60 y&\displaystyle 3 x y \left(28 x^{2} - 21 x y - 18 x - 84 y^{2} + 78 y - 10\right)\\\displaystyle 3 x y \left(28 x^{2} - 21 x y - 18 x - 84 y^{2} + 78 y - 10\right)&\displaystyle y^{2} \left(- 126 x^{2} + 42 x y + 54 x + 63 y^{2} - 78 y + 15\right)\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with edge 1 of the reference cell.
\(\displaystyle l_{18}:\boldsymbol{V}\mapsto\displaystyle\int_{e_{1}}(s_{0} \left(2 s_{0} - 1\right))\left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle 1\end{array}\right)^{\text{t}}\boldsymbol{V}\left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle -1\\\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right)\)
where \(e_{1}\) is the 1st edge;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(e_{1}\).
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{18} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle x \left(17 x^{3} - 402 x^{2} y + 38 x^{2} - 1914 x y^{2} + 1266 x y - 115 x - 1680 y^{3} + 2340 y^{2} - 840 y + 60\right)&\displaystyle y \left(- 68 x^{3} + 603 x^{2} y - 114 x^{2} + 1276 x y^{2} - 1266 x y + 230 x + 420 y^{3} - 780 y^{2} + 420 y - 60\right)\\\displaystyle y \left(- 68 x^{3} + 603 x^{2} y - 114 x^{2} + 1276 x y^{2} - 1266 x y + 230 x + 420 y^{3} - 780 y^{2} + 420 y - 60\right)&\displaystyle y \left(102 x^{2} y - 402 x y^{2} + 114 x y - 319 y^{3} + 482 y^{2} - 175 y + 12\right)\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with edge 1 of the reference cell.
where \(e_{1}\) is the 1st edge;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(e_{1}\).
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{18} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle x \left(17 x^{3} - 402 x^{2} y + 38 x^{2} - 1914 x y^{2} + 1266 x y - 115 x - 1680 y^{3} + 2340 y^{2} - 840 y + 60\right)&\displaystyle y \left(- 68 x^{3} + 603 x^{2} y - 114 x^{2} + 1276 x y^{2} - 1266 x y + 230 x + 420 y^{3} - 780 y^{2} + 420 y - 60\right)\\\displaystyle y \left(- 68 x^{3} + 603 x^{2} y - 114 x^{2} + 1276 x y^{2} - 1266 x y + 230 x + 420 y^{3} - 780 y^{2} + 420 y - 60\right)&\displaystyle y \left(102 x^{2} y - 402 x y^{2} + 114 x y - 319 y^{3} + 482 y^{2} - 175 y + 12\right)\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with edge 1 of the reference cell.
\(\displaystyle l_{19}:\boldsymbol{V}\mapsto\displaystyle\int_{e_{1}}(4 s_{0} \left(1 - s_{0}\right))\left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle -1\\\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right)^{\text{t}}\boldsymbol{V}\left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle -1\\\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right)\)
where \(e_{1}\) is the 1st edge;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(e_{1}\).
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{19} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle - x^{4} - 48 x^{3} y - 7 x^{3} - 132 x^{2} y^{2} + 141 x^{2} y + 5 x^{2} + 90 x y^{2} - 90 x y + 3 x + 105 y^{4} - 210 y^{3} + 120 y^{2} - 15 y&\displaystyle 4 x y \left(x^{2} + 18 x y - 6 x + 22 y^{2} - 24 y + 5\right)\\\displaystyle 4 x y \left(x^{2} + 18 x y - 6 x + 22 y^{2} - 24 y + 5\right)&\displaystyle y^{2} \left(- 6 x^{2} - 48 x y + 24 x - 22 y^{2} + 32 y - 10\right)\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with edge 1 of the reference cell.
where \(e_{1}\) is the 1st edge;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(e_{1}\).
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{19} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle - x^{4} - 48 x^{3} y - 7 x^{3} - 132 x^{2} y^{2} + 141 x^{2} y + 5 x^{2} + 90 x y^{2} - 90 x y + 3 x + 105 y^{4} - 210 y^{3} + 120 y^{2} - 15 y&\displaystyle 4 x y \left(x^{2} + 18 x y - 6 x + 22 y^{2} - 24 y + 5\right)\\\displaystyle 4 x y \left(x^{2} + 18 x y - 6 x + 22 y^{2} - 24 y + 5\right)&\displaystyle y^{2} \left(- 6 x^{2} - 48 x y + 24 x - 22 y^{2} + 32 y - 10\right)\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with edge 1 of the reference cell.
\(\displaystyle l_{20}:\boldsymbol{V}\mapsto\displaystyle\int_{e_{1}}(4 s_{0} \left(1 - s_{0}\right))\left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle 1\end{array}\right)^{\text{t}}\boldsymbol{V}\left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle -1\\\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right)\)
where \(e_{1}\) is the 1st edge;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(e_{1}\).
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{20} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle \frac{x \left(- 17 x^{3} + 402 x^{2} y + 22 x^{2} + 1914 x y^{2} - 1266 x y + 55 x + 1680 y^{3} - 2520 y^{2} + 960 y - 60\right)}{4}&\displaystyle \frac{y \left(68 x^{3} - 603 x^{2} y - 66 x^{2} - 1276 x y^{2} + 1266 x y - 110 x - 420 y^{3} + 840 y^{2} - 480 y + 60\right)}{4}\\\displaystyle \frac{y \left(68 x^{3} - 603 x^{2} y - 66 x^{2} - 1276 x y^{2} + 1266 x y - 110 x - 420 y^{3} + 840 y^{2} - 480 y + 60\right)}{4}&\displaystyle \frac{y \left(- 102 x^{2} y + 180 x^{2} + 402 x y^{2} - 114 x y - 120 x + 319 y^{3} - 542 y^{2} + 235 y - 12\right)}{4}\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with edge 1 of the reference cell.
where \(e_{1}\) is the 1st edge;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(e_{1}\).
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{20} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle \frac{x \left(- 17 x^{3} + 402 x^{2} y + 22 x^{2} + 1914 x y^{2} - 1266 x y + 55 x + 1680 y^{3} - 2520 y^{2} + 960 y - 60\right)}{4}&\displaystyle \frac{y \left(68 x^{3} - 603 x^{2} y - 66 x^{2} - 1276 x y^{2} + 1266 x y - 110 x - 420 y^{3} + 840 y^{2} - 480 y + 60\right)}{4}\\\displaystyle \frac{y \left(68 x^{3} - 603 x^{2} y - 66 x^{2} - 1276 x y^{2} + 1266 x y - 110 x - 420 y^{3} + 840 y^{2} - 480 y + 60\right)}{4}&\displaystyle \frac{y \left(- 102 x^{2} y + 180 x^{2} + 402 x y^{2} - 114 x y - 120 x + 319 y^{3} - 542 y^{2} + 235 y - 12\right)}{4}\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with edge 1 of the reference cell.
\(\displaystyle l_{21}:\boldsymbol{V}\mapsto\displaystyle\int_{e_{2}}(2 s_{0}^{2} - 3 s_{0} + 1)\left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle - \frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\\\displaystyle - \frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\end{array}\right)^{\text{t}}\boldsymbol{V}\left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle - \frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\\\displaystyle - \frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\end{array}\right)\)
where \(e_{2}\) is the 2nd edge;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(e_{2}\).
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{21} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle \frac{x \left(- 37 x^{3} - 54 x^{2} y + 110 x^{2} - 222 x y^{2} + 150 x y - 85 x + 12\right)}{2}&\displaystyle \frac{x y \left(148 x^{2} + 81 x y - 150 x + 148 y^{2} - 150 y + 50\right)}{2}\\\displaystyle \frac{x y \left(148 x^{2} + 81 x y - 150 x + 148 y^{2} - 150 y + 50\right)}{2}&\displaystyle \frac{y \left(- 222 x^{2} y + 180 x^{2} - 54 x y^{2} + 150 x y - 120 x - 37 y^{3} + 50 y^{2} - 25 y + 12\right)}{2}\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with edge 2 of the reference cell.
where \(e_{2}\) is the 2nd edge;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(e_{2}\).
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{21} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle \frac{x \left(- 37 x^{3} - 54 x^{2} y + 110 x^{2} - 222 x y^{2} + 150 x y - 85 x + 12\right)}{2}&\displaystyle \frac{x y \left(148 x^{2} + 81 x y - 150 x + 148 y^{2} - 150 y + 50\right)}{2}\\\displaystyle \frac{x y \left(148 x^{2} + 81 x y - 150 x + 148 y^{2} - 150 y + 50\right)}{2}&\displaystyle \frac{y \left(- 222 x^{2} y + 180 x^{2} - 54 x y^{2} + 150 x y - 120 x - 37 y^{3} + 50 y^{2} - 25 y + 12\right)}{2}\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with edge 2 of the reference cell.
\(\displaystyle l_{22}:\boldsymbol{V}\mapsto\displaystyle\int_{e_{2}}(2 s_{0}^{2} - 3 s_{0} + 1)\left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle - \frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\\\displaystyle \frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\end{array}\right)^{\text{t}}\boldsymbol{V}\left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle - \frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\\\displaystyle - \frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\end{array}\right)\)
where \(e_{2}\) is the 2nd edge;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(e_{2}\).
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{22} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle \frac{x \left(109 x^{3} + 150 x^{2} y - 86 x^{2} - 354 x y^{2} + 138 x y - 35 x + 12\right)}{2}&\displaystyle \frac{x y \left(- 436 x^{2} - 225 x y + 438 x + 236 y^{2} - 138 y - 50\right)}{2}\\\displaystyle \frac{x y \left(- 436 x^{2} - 225 x y + 438 x + 236 y^{2} - 138 y - 50\right)}{2}&\displaystyle \frac{y \left(654 x^{2} y - 180 x^{2} + 150 x y^{2} - 438 x y + 120 x - 59 y^{3} + 46 y^{2} + 25 y - 12\right)}{2}\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with edge 2 of the reference cell.
where \(e_{2}\) is the 2nd edge;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(e_{2}\).
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{22} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle \frac{x \left(109 x^{3} + 150 x^{2} y - 86 x^{2} - 354 x y^{2} + 138 x y - 35 x + 12\right)}{2}&\displaystyle \frac{x y \left(- 436 x^{2} - 225 x y + 438 x + 236 y^{2} - 138 y - 50\right)}{2}\\\displaystyle \frac{x y \left(- 436 x^{2} - 225 x y + 438 x + 236 y^{2} - 138 y - 50\right)}{2}&\displaystyle \frac{y \left(654 x^{2} y - 180 x^{2} + 150 x y^{2} - 438 x y + 120 x - 59 y^{3} + 46 y^{2} + 25 y - 12\right)}{2}\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with edge 2 of the reference cell.
\(\displaystyle l_{23}:\boldsymbol{V}\mapsto\displaystyle\int_{e_{2}}(s_{0} \left(2 s_{0} - 1\right))\left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle - \frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\\\displaystyle - \frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\end{array}\right)^{\text{t}}\boldsymbol{V}\left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle - \frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\\\displaystyle - \frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\end{array}\right)\)
where \(e_{2}\) is the 2nd edge;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(e_{2}\).
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{23} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle \frac{x \left(- 37 x^{3} - 54 x^{2} y + 50 x^{2} - 222 x y^{2} + 150 x y - 25 x + 180 y^{2} - 120 y + 12\right)}{2}&\displaystyle \frac{x y \left(148 x^{2} + 81 x y - 150 x + 148 y^{2} - 150 y + 50\right)}{2}\\\displaystyle \frac{x y \left(148 x^{2} + 81 x y - 150 x + 148 y^{2} - 150 y + 50\right)}{2}&\displaystyle \frac{y \left(- 222 x^{2} y - 54 x y^{2} + 150 x y - 37 y^{3} + 110 y^{2} - 85 y + 12\right)}{2}\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with edge 2 of the reference cell.
where \(e_{2}\) is the 2nd edge;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(e_{2}\).
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{23} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle \frac{x \left(- 37 x^{3} - 54 x^{2} y + 50 x^{2} - 222 x y^{2} + 150 x y - 25 x + 180 y^{2} - 120 y + 12\right)}{2}&\displaystyle \frac{x y \left(148 x^{2} + 81 x y - 150 x + 148 y^{2} - 150 y + 50\right)}{2}\\\displaystyle \frac{x y \left(148 x^{2} + 81 x y - 150 x + 148 y^{2} - 150 y + 50\right)}{2}&\displaystyle \frac{y \left(- 222 x^{2} y - 54 x y^{2} + 150 x y - 37 y^{3} + 110 y^{2} - 85 y + 12\right)}{2}\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with edge 2 of the reference cell.
\(\displaystyle l_{24}:\boldsymbol{V}\mapsto\displaystyle\int_{e_{2}}(s_{0} \left(2 s_{0} - 1\right))\left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle - \frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\\\displaystyle \frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\end{array}\right)^{\text{t}}\boldsymbol{V}\left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle - \frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\\\displaystyle - \frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\end{array}\right)\)
where \(e_{2}\) is the 2nd edge;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(e_{2}\).
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{24} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle \frac{x \left(59 x^{3} - 150 x^{2} y - 46 x^{2} - 654 x y^{2} + 438 x y - 25 x + 180 y^{2} - 120 y + 12\right)}{2}&\displaystyle \frac{x y \left(- 236 x^{2} + 225 x y + 138 x + 436 y^{2} - 438 y + 50\right)}{2}\\\displaystyle \frac{x y \left(- 236 x^{2} + 225 x y + 138 x + 436 y^{2} - 438 y + 50\right)}{2}&\displaystyle \frac{y \left(354 x^{2} y - 150 x y^{2} - 138 x y - 109 y^{3} + 86 y^{2} + 35 y - 12\right)}{2}\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with edge 2 of the reference cell.
where \(e_{2}\) is the 2nd edge;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(e_{2}\).
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{24} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle \frac{x \left(59 x^{3} - 150 x^{2} y - 46 x^{2} - 654 x y^{2} + 438 x y - 25 x + 180 y^{2} - 120 y + 12\right)}{2}&\displaystyle \frac{x y \left(- 236 x^{2} + 225 x y + 138 x + 436 y^{2} - 438 y + 50\right)}{2}\\\displaystyle \frac{x y \left(- 236 x^{2} + 225 x y + 138 x + 436 y^{2} - 438 y + 50\right)}{2}&\displaystyle \frac{y \left(354 x^{2} y - 150 x y^{2} - 138 x y - 109 y^{3} + 86 y^{2} + 35 y - 12\right)}{2}\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with edge 2 of the reference cell.
\(\displaystyle l_{25}:\boldsymbol{V}\mapsto\displaystyle\int_{e_{2}}(4 s_{0} \left(1 - s_{0}\right))\left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle - \frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\\\displaystyle - \frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\end{array}\right)^{\text{t}}\boldsymbol{V}\left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle - \frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\\\displaystyle - \frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\end{array}\right)\)
where \(e_{2}\) is the 2nd edge;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(e_{2}\).
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{25} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle \frac{x \left(- 19 x^{3} - 198 x^{2} y + 80 x^{2} - 114 x y^{2} + 330 x y - 85 x + 90 y^{2} - 120 y + 24\right)}{4}&\displaystyle \frac{x y \left(76 x^{2} + 297 x y - 150 x + 76 y^{2} - 150 y + 50\right)}{4}\\\displaystyle \frac{x y \left(76 x^{2} + 297 x y - 150 x + 76 y^{2} - 150 y + 50\right)}{4}&\displaystyle \frac{y \left(- 114 x^{2} y + 90 x^{2} - 198 x y^{2} + 330 x y - 120 x - 19 y^{3} + 80 y^{2} - 85 y + 24\right)}{4}\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with edge 2 of the reference cell.
where \(e_{2}\) is the 2nd edge;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(e_{2}\).
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{25} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle \frac{x \left(- 19 x^{3} - 198 x^{2} y + 80 x^{2} - 114 x y^{2} + 330 x y - 85 x + 90 y^{2} - 120 y + 24\right)}{4}&\displaystyle \frac{x y \left(76 x^{2} + 297 x y - 150 x + 76 y^{2} - 150 y + 50\right)}{4}\\\displaystyle \frac{x y \left(76 x^{2} + 297 x y - 150 x + 76 y^{2} - 150 y + 50\right)}{4}&\displaystyle \frac{y \left(- 114 x^{2} y + 90 x^{2} - 198 x y^{2} + 330 x y - 120 x - 19 y^{3} + 80 y^{2} - 85 y + 24\right)}{4}\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with edge 2 of the reference cell.
\(\displaystyle l_{26}:\boldsymbol{V}\mapsto\displaystyle\int_{e_{2}}(4 s_{0} \left(1 - s_{0}\right))\left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle - \frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\\\displaystyle \frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\end{array}\right)^{\text{t}}\boldsymbol{V}\left(\begin{array}{c}\displaystyle - \frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\\\displaystyle - \frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\end{array}\right)\)
where \(e_{2}\) is the 2nd edge;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(e_{2}\).
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{26} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle \frac{3 x \left(- 7 x^{3} + 13 x^{2} + 42 x y^{2} + 6 x y - 10 x + 15 y^{2} - 20 y + 4\right)}{2}&\displaystyle 6 x y \left(7 x^{2} - 6 x - 7 y^{2} + 6 y\right)\\\displaystyle 6 x y \left(7 x^{2} - 6 x - 7 y^{2} + 6 y\right)&\displaystyle \frac{3 y \left(- 42 x^{2} y - 15 x^{2} - 6 x y + 20 x + 7 y^{3} - 13 y^{2} + 10 y - 4\right)}{2}\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with edge 2 of the reference cell.
where \(e_{2}\) is the 2nd edge;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(e_{2}\).
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{26} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle \frac{3 x \left(- 7 x^{3} + 13 x^{2} + 42 x y^{2} + 6 x y - 10 x + 15 y^{2} - 20 y + 4\right)}{2}&\displaystyle 6 x y \left(7 x^{2} - 6 x - 7 y^{2} + 6 y\right)\\\displaystyle 6 x y \left(7 x^{2} - 6 x - 7 y^{2} + 6 y\right)&\displaystyle \frac{3 y \left(- 42 x^{2} y - 15 x^{2} - 6 x y + 20 x + 7 y^{3} - 13 y^{2} + 10 y - 4\right)}{2}\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with edge 2 of the reference cell.
\(\displaystyle l_{27}:v\mapsto\displaystyle\int_{R}(\left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle - s_{0} - s_{1} + 1&\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right))v\)
where \(R\) is the reference element;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(R\).
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{27} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 10 x \left(- 5 x^{3} - 30 x^{2} y + 46 x^{2} - 30 x y^{2} + 102 x y - 65 x + 36 y^{2} - 60 y + 24\right)&\displaystyle 50 x y \left(4 x^{2} + 9 x y - 6 x + 4 y^{2} - 6 y + 2\right)\\\displaystyle 50 x y \left(4 x^{2} + 9 x y - 6 x + 4 y^{2} - 6 y + 2\right)&\displaystyle 50 y^{2} \left(- 6 x^{2} - 6 x y + 6 x - y^{2} + 2 y - 1\right)\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with face 0 of the reference cell.
where \(R\) is the reference element;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(R\).
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{27} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 10 x \left(- 5 x^{3} - 30 x^{2} y + 46 x^{2} - 30 x y^{2} + 102 x y - 65 x + 36 y^{2} - 60 y + 24\right)&\displaystyle 50 x y \left(4 x^{2} + 9 x y - 6 x + 4 y^{2} - 6 y + 2\right)\\\displaystyle 50 x y \left(4 x^{2} + 9 x y - 6 x + 4 y^{2} - 6 y + 2\right)&\displaystyle 50 y^{2} \left(- 6 x^{2} - 6 x y + 6 x - y^{2} + 2 y - 1\right)\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with face 0 of the reference cell.
\(\displaystyle l_{28}:v\mapsto\displaystyle\int_{R}(\left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle - s_{0} - s_{1} + 1\\\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right))v\)
where \(R\) is the reference element;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(R\).
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{28} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 30 x \left(- 15 x^{3} - 90 x^{2} y + 42 x^{2} - 90 x y^{2} + 138 x y - 35 x + 36 y^{2} - 40 y + 8\right)&\displaystyle 30 x y \left(60 x^{2} + 135 x y - 114 x + 60 y^{2} - 114 y + 50\right)\\\displaystyle 30 x y \left(60 x^{2} + 135 x y - 114 x + 60 y^{2} - 114 y + 50\right)&\displaystyle 30 y \left(- 90 x^{2} y + 36 x^{2} - 90 x y^{2} + 138 x y - 40 x - 15 y^{3} + 42 y^{2} - 35 y + 8\right)\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with face 0 of the reference cell.
where \(R\) is the reference element;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(R\).
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{28} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 30 x \left(- 15 x^{3} - 90 x^{2} y + 42 x^{2} - 90 x y^{2} + 138 x y - 35 x + 36 y^{2} - 40 y + 8\right)&\displaystyle 30 x y \left(60 x^{2} + 135 x y - 114 x + 60 y^{2} - 114 y + 50\right)\\\displaystyle 30 x y \left(60 x^{2} + 135 x y - 114 x + 60 y^{2} - 114 y + 50\right)&\displaystyle 30 y \left(- 90 x^{2} y + 36 x^{2} - 90 x y^{2} + 138 x y - 40 x - 15 y^{3} + 42 y^{2} - 35 y + 8\right)\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with face 0 of the reference cell.
\(\displaystyle l_{29}:v\mapsto\displaystyle\int_{R}(\left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle - s_{0} - s_{1} + 1\end{array}\right))v\)
where \(R\) is the reference element;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(R\).
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{29} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 50 x^{2} \left(- x^{2} - 6 x y + 2 x - 6 y^{2} + 6 y - 1\right)&\displaystyle 50 x y \left(4 x^{2} + 9 x y - 6 x + 4 y^{2} - 6 y + 2\right)\\\displaystyle 50 x y \left(4 x^{2} + 9 x y - 6 x + 4 y^{2} - 6 y + 2\right)&\displaystyle 10 y \left(- 30 x^{2} y + 36 x^{2} - 30 x y^{2} + 102 x y - 60 x - 5 y^{3} + 46 y^{2} - 65 y + 24\right)\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with face 0 of the reference cell.
where \(R\) is the reference element;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(R\).
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{29} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 50 x^{2} \left(- x^{2} - 6 x y + 2 x - 6 y^{2} + 6 y - 1\right)&\displaystyle 50 x y \left(4 x^{2} + 9 x y - 6 x + 4 y^{2} - 6 y + 2\right)\\\displaystyle 50 x y \left(4 x^{2} + 9 x y - 6 x + 4 y^{2} - 6 y + 2\right)&\displaystyle 10 y \left(- 30 x^{2} y + 36 x^{2} - 30 x y^{2} + 102 x y - 60 x - 5 y^{3} + 46 y^{2} - 65 y + 24\right)\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with face 0 of the reference cell.
\(\displaystyle l_{30}:v\mapsto\displaystyle\int_{R}(\left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle s_{0}&\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right))v\)
where \(R\) is the reference element;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(R\).
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{30} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 120 x \left(- 3 x^{2} - 3 x y + 4 x + y - 1\right)&\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with face 0 of the reference cell.
where \(R\) is the reference element;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(R\).
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{30} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 120 x \left(- 3 x^{2} - 3 x y + 4 x + y - 1\right)&\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with face 0 of the reference cell.
\(\displaystyle l_{31}:v\mapsto\displaystyle\int_{R}(\left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle s_{0}\\\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right))v\)
where \(R\) is the reference element;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(R\).
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{31} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 40 x \left(5 x^{3} + 30 x^{2} y - 19 x^{2} + 30 x y^{2} - 48 x y + 17 x + 6 y - 3\right)&\displaystyle 40 x y \left(- 20 x^{2} - 45 x y + 39 x - 20 y^{2} + 30 y - 13\right)\\\displaystyle 40 x y \left(- 20 x^{2} - 45 x y + 39 x - 20 y^{2} + 30 y - 13\right)&\displaystyle 40 y \left(30 x^{2} y - 27 x^{2} + 30 x y^{2} - 48 x y + 24 x + 5 y^{3} - 10 y^{2} + 8 y - 3\right)\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with face 0 of the reference cell.
where \(R\) is the reference element;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(R\).
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{31} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 40 x \left(5 x^{3} + 30 x^{2} y - 19 x^{2} + 30 x y^{2} - 48 x y + 17 x + 6 y - 3\right)&\displaystyle 40 x y \left(- 20 x^{2} - 45 x y + 39 x - 20 y^{2} + 30 y - 13\right)\\\displaystyle 40 x y \left(- 20 x^{2} - 45 x y + 39 x - 20 y^{2} + 30 y - 13\right)&\displaystyle 40 y \left(30 x^{2} y - 27 x^{2} + 30 x y^{2} - 48 x y + 24 x + 5 y^{3} - 10 y^{2} + 8 y - 3\right)\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with face 0 of the reference cell.
\(\displaystyle l_{32}:v\mapsto\displaystyle\int_{R}(\left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle s_{0}\end{array}\right))v\)
where \(R\) is the reference element;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(R\).
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{32} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 100 x^{2} \left(x^{2} + 6 x y - 2 x + 6 y^{2} - 6 y + 1\right)&\displaystyle 100 x y \left(- 4 x^{2} - 9 x y + 6 x - 4 y^{2} + 6 y - 2\right)\\\displaystyle 100 x y \left(- 4 x^{2} - 9 x y + 6 x - 4 y^{2} + 6 y - 2\right)&\displaystyle 20 y \left(30 x^{2} y - 36 x^{2} + 30 x y^{2} - 66 x y + 42 x + 5 y^{3} - 10 y^{2} + 11 y - 6\right)\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with face 0 of the reference cell.
where \(R\) is the reference element;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(R\).
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{32} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 100 x^{2} \left(x^{2} + 6 x y - 2 x + 6 y^{2} - 6 y + 1\right)&\displaystyle 100 x y \left(- 4 x^{2} - 9 x y + 6 x - 4 y^{2} + 6 y - 2\right)\\\displaystyle 100 x y \left(- 4 x^{2} - 9 x y + 6 x - 4 y^{2} + 6 y - 2\right)&\displaystyle 20 y \left(30 x^{2} y - 36 x^{2} + 30 x y^{2} - 66 x y + 42 x + 5 y^{3} - 10 y^{2} + 11 y - 6\right)\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with face 0 of the reference cell.
\(\displaystyle l_{33}:v\mapsto\displaystyle\int_{R}(\left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle s_{1}&\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right))v\)
where \(R\) is the reference element;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(R\).
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{33} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 20 x \left(5 x^{3} + 30 x^{2} y - 10 x^{2} + 30 x y^{2} - 66 x y + 11 x - 36 y^{2} + 42 y - 6\right)&\displaystyle 100 x y \left(- 4 x^{2} - 9 x y + 6 x - 4 y^{2} + 6 y - 2\right)\\\displaystyle 100 x y \left(- 4 x^{2} - 9 x y + 6 x - 4 y^{2} + 6 y - 2\right)&\displaystyle 100 y^{2} \left(6 x^{2} + 6 x y - 6 x + y^{2} - 2 y + 1\right)\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with face 0 of the reference cell.
where \(R\) is the reference element;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(R\).
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{33} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 20 x \left(5 x^{3} + 30 x^{2} y - 10 x^{2} + 30 x y^{2} - 66 x y + 11 x - 36 y^{2} + 42 y - 6\right)&\displaystyle 100 x y \left(- 4 x^{2} - 9 x y + 6 x - 4 y^{2} + 6 y - 2\right)\\\displaystyle 100 x y \left(- 4 x^{2} - 9 x y + 6 x - 4 y^{2} + 6 y - 2\right)&\displaystyle 100 y^{2} \left(6 x^{2} + 6 x y - 6 x + y^{2} - 2 y + 1\right)\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with face 0 of the reference cell.
\(\displaystyle l_{34}:v\mapsto\displaystyle\int_{R}(\left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle s_{1}\\\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle 0\end{array}\right))v\)
where \(R\) is the reference element;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(R\).
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{34} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 40 x \left(5 x^{3} + 30 x^{2} y - 10 x^{2} + 30 x y^{2} - 48 x y + 8 x - 27 y^{2} + 24 y - 3\right)&\displaystyle 40 x y \left(- 20 x^{2} - 45 x y + 30 x - 20 y^{2} + 39 y - 13\right)\\\displaystyle 40 x y \left(- 20 x^{2} - 45 x y + 30 x - 20 y^{2} + 39 y - 13\right)&\displaystyle 40 y \left(30 x^{2} y + 30 x y^{2} - 48 x y + 6 x + 5 y^{3} - 19 y^{2} + 17 y - 3\right)\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with face 0 of the reference cell.
where \(R\) is the reference element;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(R\).
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{34} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 40 x \left(5 x^{3} + 30 x^{2} y - 10 x^{2} + 30 x y^{2} - 48 x y + 8 x - 27 y^{2} + 24 y - 3\right)&\displaystyle 40 x y \left(- 20 x^{2} - 45 x y + 30 x - 20 y^{2} + 39 y - 13\right)\\\displaystyle 40 x y \left(- 20 x^{2} - 45 x y + 30 x - 20 y^{2} + 39 y - 13\right)&\displaystyle 40 y \left(30 x^{2} y + 30 x y^{2} - 48 x y + 6 x + 5 y^{3} - 19 y^{2} + 17 y - 3\right)\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with face 0 of the reference cell.
\(\displaystyle l_{35}:v\mapsto\displaystyle\int_{R}(\left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle s_{1}\end{array}\right))v\)
where \(R\) is the reference element;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(R\).
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{35} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle 120 y \left(- 3 x y + x - 3 y^{2} + 4 y - 1\right)\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with face 0 of the reference cell.
where \(R\) is the reference element;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(R\).
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{35} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle 0\\\displaystyle 0&\displaystyle 120 y \left(- 3 x y + x - 3 y^{2} + 4 y - 1\right)\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with face 0 of the reference cell.
\(\displaystyle l_{36}:v\mapsto\displaystyle\int_{R}(\left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 2 s_{0}^{2} \left(s_{0}^{2} + 6 s_{0} s_{1} - 2 s_{0} + 6 s_{1}^{2} - 6 s_{1} + 1\right)&\displaystyle 2 s_{0} s_{1} \left(- 4 s_{0}^{2} - 9 s_{0} s_{1} + 6 s_{0} - 4 s_{1}^{2} + 6 s_{1} - 2\right)\\\displaystyle 2 s_{0} s_{1} \left(- 4 s_{0}^{2} - 9 s_{0} s_{1} + 6 s_{0} - 4 s_{1}^{2} + 6 s_{1} - 2\right)&\displaystyle 2 s_{1}^{2} \left(6 s_{0}^{2} + 6 s_{0} s_{1} - 6 s_{0} + s_{1}^{2} - 2 s_{1} + 1\right)\end{array}\right))v\)
where \(R\) is the reference element;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(R\).
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{36} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 1050 x^{2} \left(x^{2} + 6 x y - 2 x + 6 y^{2} - 6 y + 1\right)&\displaystyle 1050 x y \left(- 4 x^{2} - 9 x y + 6 x - 4 y^{2} + 6 y - 2\right)\\\displaystyle 1050 x y \left(- 4 x^{2} - 9 x y + 6 x - 4 y^{2} + 6 y - 2\right)&\displaystyle 1050 y^{2} \left(6 x^{2} + 6 x y - 6 x + y^{2} - 2 y + 1\right)\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with face 0 of the reference cell.
where \(R\) is the reference element;
and \(s_{0},s_{1}\) is a parametrisation of \(R\).
\(\displaystyle \mathbf{\Phi}_{36} = \left(\begin{array}{cc}\displaystyle 1050 x^{2} \left(x^{2} + 6 x y - 2 x + 6 y^{2} - 6 y + 1\right)&\displaystyle 1050 x y \left(- 4 x^{2} - 9 x y + 6 x - 4 y^{2} + 6 y - 2\right)\\\displaystyle 1050 x y \left(- 4 x^{2} - 9 x y + 6 x - 4 y^{2} + 6 y - 2\right)&\displaystyle 1050 y^{2} \left(6 x^{2} + 6 x y - 6 x + y^{2} - 2 y + 1\right)\end{array}\right)\)
This DOF is associated with face 0 of the reference cell.