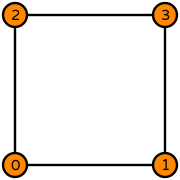
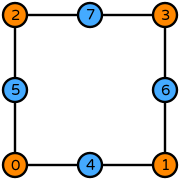
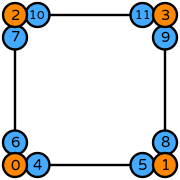
| Basix | basix.ElementFamily.serendipity, lagrange_variant=basix.LagrangeVariant.equispaced, dpc_variant=basix.DPCVariant.simplex_equispaced
↓ Show Basix examples ↓↑ Hide Basix examples ↑Before running this example, you must install Basix: pip install fenics-basix This element can then be created with the following lines of Python: import basix
# Create serendipity degree 1 on a interval
element = basix.create_element(basix.ElementFamily.serendipity, basix.CellType.interval, 1, lagrange_variant=basix.LagrangeVariant.equispaced, dpc_variant=basix.DPCVariant.simplex_equispaced)
# Create serendipity degree 2 on a interval
element = basix.create_element(basix.ElementFamily.serendipity, basix.CellType.interval, 2, lagrange_variant=basix.LagrangeVariant.equispaced, dpc_variant=basix.DPCVariant.simplex_equispaced)
# Create serendipity degree 3 on a interval
element = basix.create_element(basix.ElementFamily.serendipity, basix.CellType.interval, 3, lagrange_variant=basix.LagrangeVariant.equispaced, dpc_variant=basix.DPCVariant.simplex_equispaced)
# Create serendipity degree 1 on a quadrilateral
element = basix.create_element(basix.ElementFamily.serendipity, basix.CellType.quadrilateral, 1, lagrange_variant=basix.LagrangeVariant.equispaced, dpc_variant=basix.DPCVariant.simplex_equispaced)
# Create serendipity degree 2 on a quadrilateral
element = basix.create_element(basix.ElementFamily.serendipity, basix.CellType.quadrilateral, 2, lagrange_variant=basix.LagrangeVariant.equispaced, dpc_variant=basix.DPCVariant.simplex_equispaced)
# Create serendipity degree 3 on a quadrilateral
element = basix.create_element(basix.ElementFamily.serendipity, basix.CellType.quadrilateral, 3, lagrange_variant=basix.LagrangeVariant.equispaced, dpc_variant=basix.DPCVariant.simplex_equispaced) |
| Basix.UFL | basix.ElementFamily.serendipity, lagrange_variant=basix.LagrangeVariant.equispaced, dpc_variant=basix.DPCVariant.simplex_equispaced
↓ Show Basix.UFL examples ↓↑ Hide Basix.UFL examples ↑Before running this example, you must install Basix.UFL: pip install fenics-ufl
pip install fenics-basix This element can then be created with the following lines of Python: import basix
import basix.ufl
# Create serendipity degree 1 on a interval
element = basix.ufl.element(basix.ElementFamily.serendipity, basix.CellType.interval, 1, lagrange_variant=basix.LagrangeVariant.equispaced, dpc_variant=basix.DPCVariant.simplex_equispaced)
# Create serendipity degree 2 on a interval
element = basix.ufl.element(basix.ElementFamily.serendipity, basix.CellType.interval, 2, lagrange_variant=basix.LagrangeVariant.equispaced, dpc_variant=basix.DPCVariant.simplex_equispaced)
# Create serendipity degree 3 on a interval
element = basix.ufl.element(basix.ElementFamily.serendipity, basix.CellType.interval, 3, lagrange_variant=basix.LagrangeVariant.equispaced, dpc_variant=basix.DPCVariant.simplex_equispaced)
# Create serendipity degree 1 on a quadrilateral
element = basix.ufl.element(basix.ElementFamily.serendipity, basix.CellType.quadrilateral, 1, lagrange_variant=basix.LagrangeVariant.equispaced, dpc_variant=basix.DPCVariant.simplex_equispaced)
# Create serendipity degree 2 on a quadrilateral
element = basix.ufl.element(basix.ElementFamily.serendipity, basix.CellType.quadrilateral, 2, lagrange_variant=basix.LagrangeVariant.equispaced, dpc_variant=basix.DPCVariant.simplex_equispaced)
# Create serendipity degree 3 on a quadrilateral
element = basix.ufl.element(basix.ElementFamily.serendipity, basix.CellType.quadrilateral, 3, lagrange_variant=basix.LagrangeVariant.equispaced, dpc_variant=basix.DPCVariant.simplex_equispaced) |
| FIAT | FIAT.Serendipity
↓ Show FIAT examples ↓↑ Hide FIAT examples ↑Before running this example, you must install FIAT: pip install firedrake-fiat This element can then be created with the following lines of Python: import FIAT
# Create serendipity degree 1 on a interval
element = FIAT.Serendipity(FIAT.ufc_cell("interval"), 1)
# Create serendipity degree 2 on a interval
element = FIAT.Serendipity(FIAT.ufc_cell("interval"), 2)
# Create serendipity degree 3 on a interval
element = FIAT.Serendipity(FIAT.ufc_cell("interval"), 3)
# Create serendipity degree 1 on a quadrilateral
element = FIAT.Serendipity(FIAT.reference_element.UFCQuadrilateral(), 1)
# Create serendipity degree 2 on a quadrilateral
element = FIAT.Serendipity(FIAT.reference_element.UFCQuadrilateral(), 2)
# Create serendipity degree 3 on a quadrilateral
element = FIAT.Serendipity(FIAT.reference_element.UFCQuadrilateral(), 3) |
| Symfem | "serendipity"
↓ Show Symfem examples ↓↑ Hide Symfem examples ↑Before running this example, you must install Symfem: pip install symfem This element can then be created with the following lines of Python: import symfem
# Create serendipity degree 1 on a interval
element = symfem.create_element("interval", "serendipity", 1)
# Create serendipity degree 2 on a interval
element = symfem.create_element("interval", "serendipity", 2)
# Create serendipity degree 3 on a interval
element = symfem.create_element("interval", "serendipity", 3)
# Create serendipity degree 1 on a quadrilateral
element = symfem.create_element("quadrilateral", "serendipity", 1)
# Create serendipity degree 2 on a quadrilateral
element = symfem.create_element("quadrilateral", "serendipity", 2)
# Create serendipity degree 3 on a quadrilateral
element = symfem.create_element("quadrilateral", "serendipity", 3) |